Deploying Java applications can be challenging, especially when dealing with Linux or Windows servers. From handling logs and memory issues to configuring the JVM and network settings, a smooth deployment requires careful planning. This guide will cover common Java deployment problems, JVM tuning, log management, firewall issues, and how EgyVPS can help you ensure stable and high-performance Java applications.

Ensure the Java version on the target server matches the application's requirements, such as specific Java EE versions or APIs. Running incompatible versions may cause runtime errors.
Out-of-memory errors often occur when the JVM heap is too small. Solutions include:
Increasing heap size using -Xms and -Xmx flags, e.g., java -Xms512m -Xmx1024m -jar app.jar
Checking system limits (e.g., ulimit on Linux)
Monitoring memory usage with tools like jcmd and VisualVM
Network issues and firewalls can block Java applications from accessing resources. Troubleshooting steps:
Temporarily disable firewalls or antivirus to test
Check SSL/TLS certificates to prevent handshake failures
Configure proxy settings if needed
Ensure correct servlet or library versions during build
Check for duplicate configurations
Verify all dependencies are included in the classpath
Correct ClassNotFoundException or NoClassDefFoundError by adjusting paths and dependencies
System.out / System.err: Captures standard output and errors
Fatal Error Logs (hs_err_pid*.log): Contains crash reports and memory details
Log4j / Logback / JUL / SLF4J: Frameworks for structured logging
Configured in files like log4j.properties or logback.xml
/var/log/syslog or /var/log/messages — general system events
/var/log/auth.log — security events
/var/log/kern.log — kernel errors and warnings
/var/log/cron — cron jobs
Memory leaks occur when unused objects remain referenced, leading to performance issues:
Long-lived static fields
Unclosed resources (files, DB connections)
ThreadLocal variables not removed
Non-static inner classes retaining outer references
Tools for detection:
Heap dumps with jmap analyzed using Eclipse MAT
Monitoring via VisualVM, JConsole, or AppDynamics
Verbose GC logging
Set equal minimum and maximum heap sizes using -Xms and -Xmx
Avoid exceeding physical RAM (use ~80% of free RAM)
Adjust thread stack sizes with -Xss
G1 (Garbage-First): Balances performance and response time
Parallel GC: Optimized for multi-core systems
Adjust GC pause targets (-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis)
Use adaptive sizing (-XX:+UseAdaptiveSizePolicy)
Enable Tiered Compilation (-XX:+TieredCompilation)
Inline critical methods (-XX:MaxInlineSize)
Enable aggressive optimizations (-XX:+AggressiveOpts)
Use Java Flight Recorder (JFR) and Mission Control (JMC)
Track CPU, memory, and GC metrics
Allow Java applications through firewalls (Windows Defender or third-party)
Verify proxy settings if required
Temporarily disable firewalls for testing
Review network logs for blocked connections
Reduce unnecessary if-else statements
Use StringBuilder for concatenations
Prefer primitive types over wrappers when possible
Optimize database interactions
Enable JIT compilation for runtime improvements
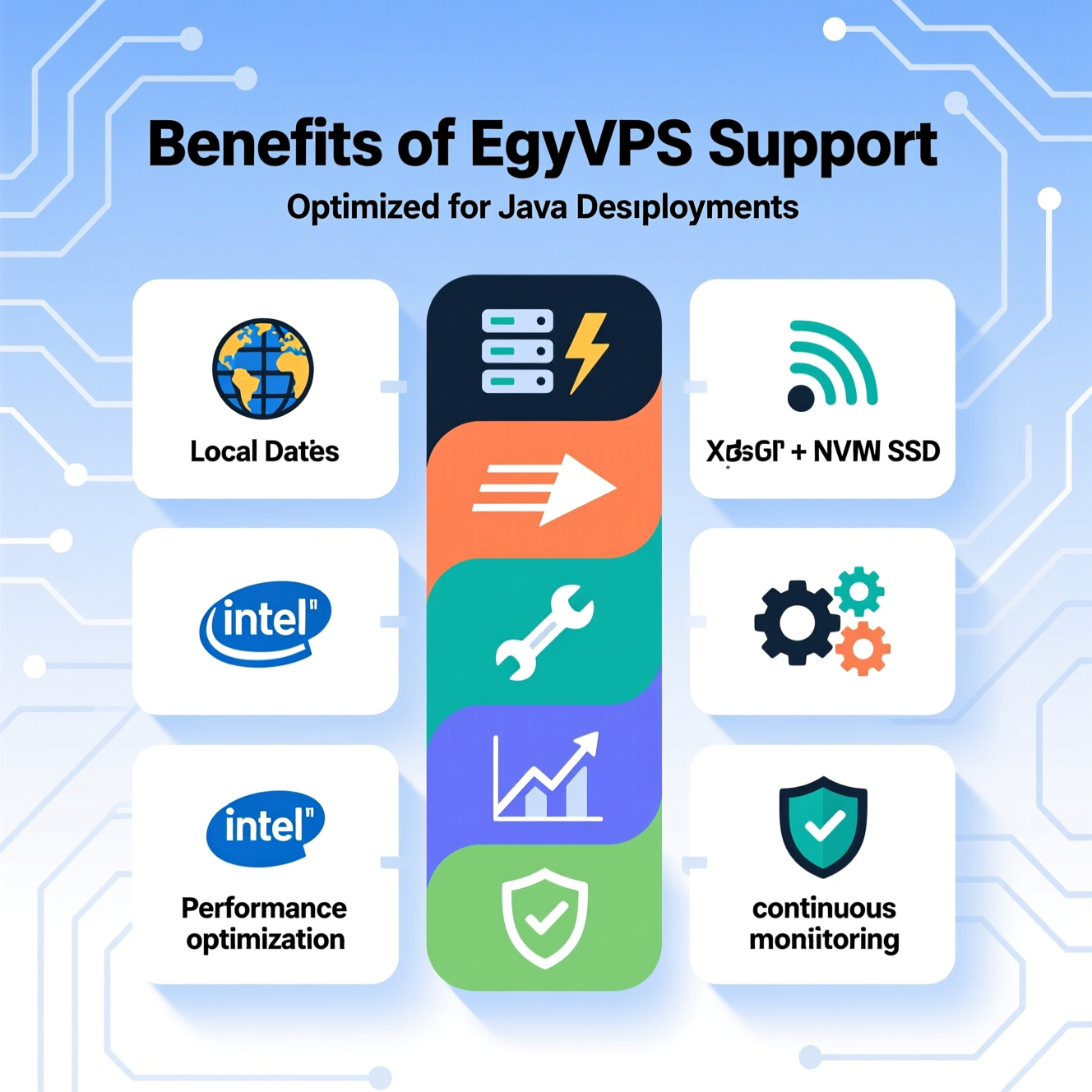
EgyVPS provides local server support for Java deployments:
Local data centers for fast response
Intel Xeon + NVMe SSD infrastructure
High-speed internet (up to 1Gbps)
Configuration support for JVM and libraries
Performance optimization and troubleshooting
Continuous monitoring and stability guarantees
|
|
Benefit |
|---|---|
| Local data centers | Reduced latency, better user experience |
| High-performance servers | Handles heavy Java workloads |
| Fast internet | Efficient data transfer |
| Technical support | Fixes errors, optimizes configuration |
| JVM tuning guidance | Improves stability and performance |
Q1: How do I check Java version on the server?
A1: Run java -version in the terminal or command prompt.
Q2: What tools can detect memory leaks?
A2: VisualVM, Eclipse MAT, JConsole, AppDynamics.
Q3: How do I fix ClassNotFoundException?
A3: Verify the classpath, ensure all dependencies are included, and check for typos in class names.
Q4: What JVM flags optimize performance?
A4: -Xms, -Xmx, -Xss, -XX:+TieredCompilation, -XX:+UseG1GC.
Q5: How can EgyVPS help with Java deployments?
A5: They provide local server support, JVM configuration guidance, performance optimization, and troubleshooting.
هل تحتاج إلى Windows VPS سريع وآمن وبسعر مناسب؟
شركة EgyVPS بتوفرلك سيرفرات ويندوز جاهزة للاستخدام فورًا.
? تواصل معنا عبر: 201001197157
? أو زور موقعنا: https://egyvps.com