RAID
Redundant Array of Independent Disks
What is RAID?
How RAID works?
RAID controller
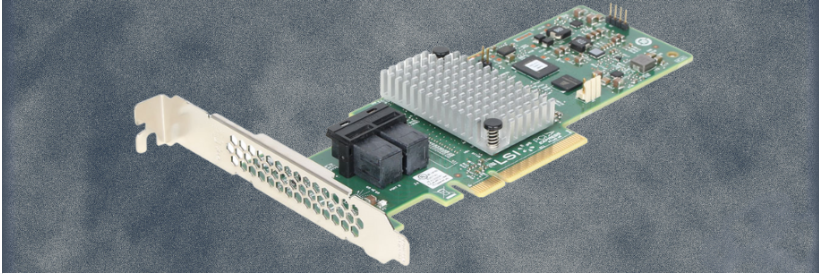
RAID levels
RAID devices use different versions, called levels.
The original paper that coined the term and developed the RAID setup concept defined six levels of RAID -- 0 through 5.
This numbered system enabled those in IT to differentiate RAID versions.
The number of levels has since expanded and has been broken into three categories: standard, nested and nonstandard RAID levels.
RAID 0
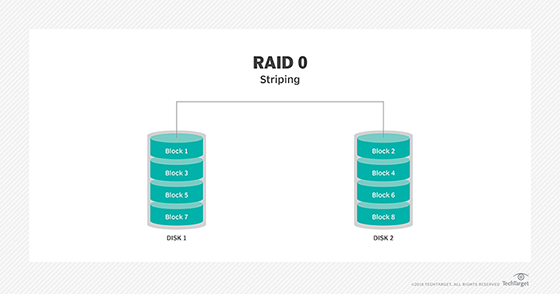
RAID 0 . This configuration has striping but no redundancy of data. It offers the best performance, but it does not provide fault tolerance.
RAID 1
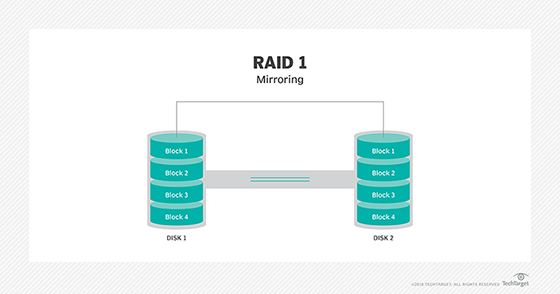
Also known as disk mirroring, this configuration consists of at least two drives that duplicate the storage of data. There is no striping. Read performance is improved since either disk can be read at the same time. Write performance is the same as for single-disk storage.
RAID 5
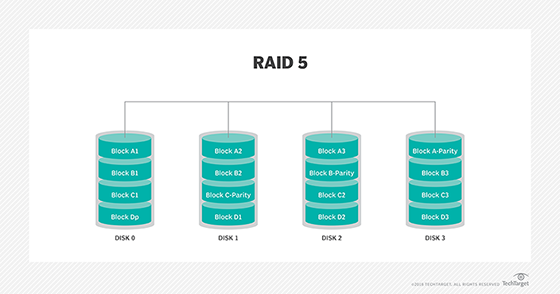
“Distributed Parity” is the key word here.
RAID 6
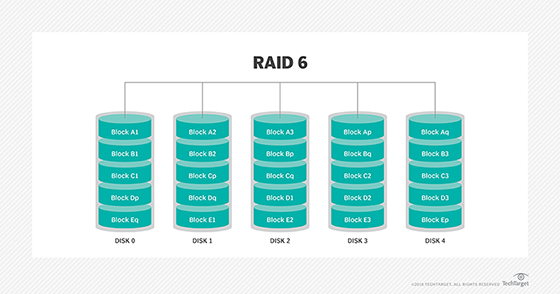
This technique is similar to RAID 5, but it includes a second parity scheme distributed across the drives in the array. The use of additional parity enables the array to continue functioning, even if two disks fail simultaneously. However, this extra protection comes at a cost. RAID 6 arrays often have slower write performance than RAID 5 arrays.
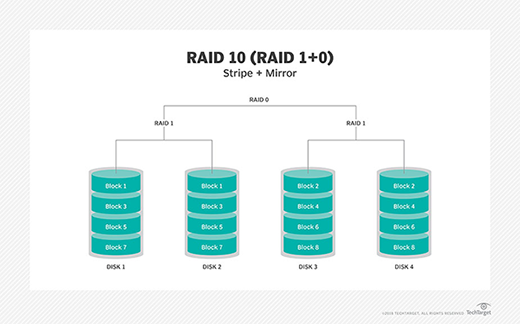
RAID 10
Benefits of RAID
Improved cost-effectiveness because lower-priced disks are used in large numbers.
Using multiple hard drives enables RAID to improve the performance of a single hard drive.
Increased computer speed and reliability after a crash, depending on the configuration.
Reads and writes can be performed faster than with a single drive with RAID 0. This is because a file system is split up and distributed across drives that work together on the same file.
There is increased availability and resiliency with RAID 5. With mirroring, two drives can contain the same data, ensuring one will continue to work if the other fails.